|
|
一
前言
前段时间在看雪上看到了研究钉钉CEF框架的帖子,认真看完了,受益匪浅:https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-274198.htm
于是我也想找一个CEF框架的应用,用同样的思路去实践一下。正好这两天面试百度,面试会议软件用的是它们自己做的“如流”,恰好也是CEF框架。
二
初步环境准备
由于后面需要用到hook手段,所以这里最好是把对应版本的cef库从官网给下载下来,如此一来,相关的结构体、类、成员的声明就不需要我们自己做了。首先打开如流安装目录下的cef目录,打开libcef.dll的属性。
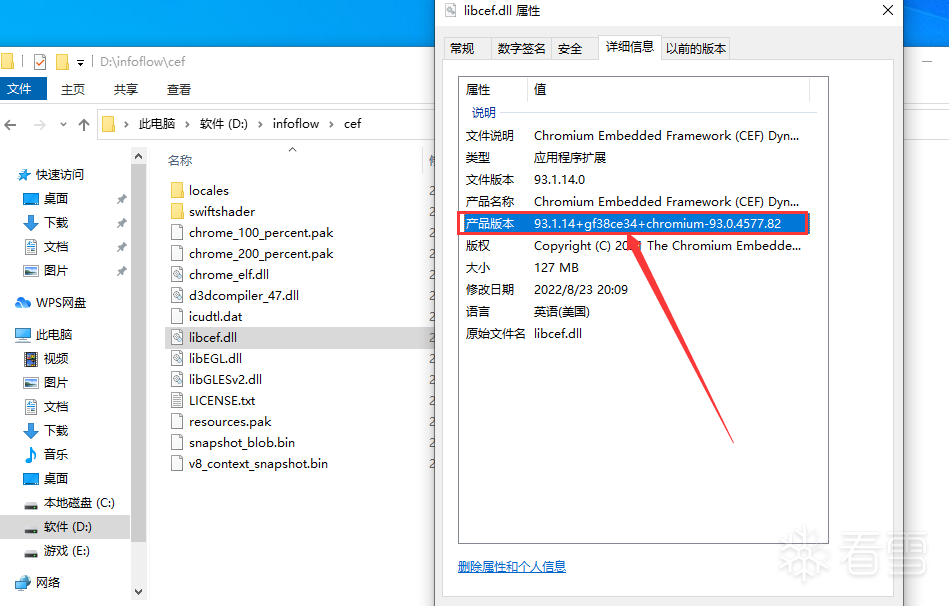
去官网找对应的libcef+chromium版本即可:https://cef-builds.spotifycdn.com/index.html下载框架
在windows上下载好后,直接解压即可。
 后面还要用到detours进行api的hook,所以把detours也装一下,顺便学习学习detours咋用:https://www.lmlphp.com/user/65200/article/item/640921/ 后面还要用到detours进行api的hook,所以把detours也装一下,顺便学习学习detours咋用:https://www.lmlphp.com/user/65200/article/item/640921/
三
找到js资源文件所在
根据参考帖,我们要在应用登录前,选择这两个函数下断点
cef_stream_reader_create_for_data
cef_stream_reader_create_for_file
本来想打开如流,然后用OD附加进程来着,结果各种问题,干脆直接以启动方式打开调试,先F9让它跑起来,等登录界面出来,在libcef.dll模块里的两个函数下断点(记得程序是这个infoflow.exe,别调成了iLauncher.exe,这是个启动器)。
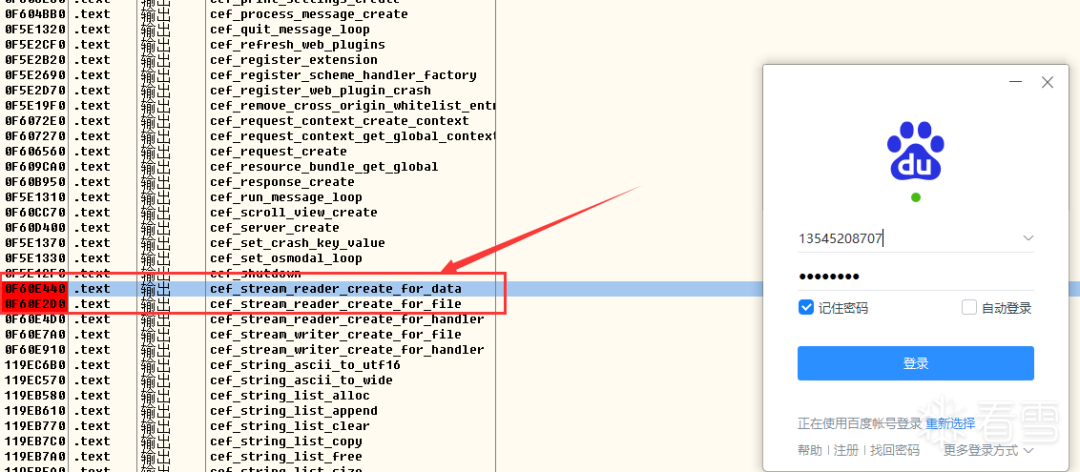
然后输入自己的账户密码登录,登录成功后,过了一会断点才来,经过测试,发现断点只断这么一次。根据寄存器ECX~EDI的值定位到内存,发现多个资源路径(所有寄存器对应内存都看一下)。
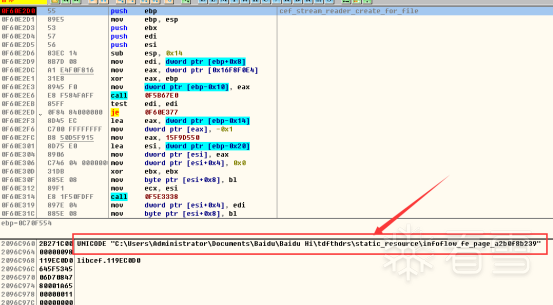
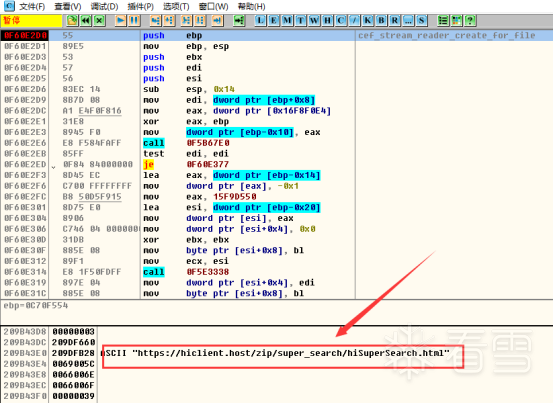
第二张和第三张图片可以省略,因为这俩资源文件在第一张路径里都有,找到第一张的路径,发现是个加密的zip。
四
解密资源文件
程序运行时肯定会在某个时机解密数据,我们在相关API处下断点,逆向分析即可得到密码。这里根据参考帖子,也是从CEF框架的API入手。
cef_zip_directory 写数据到zip文件。
cef_zip_reader_create从zip文件读取数据。
我们想要拿解压缩密码的话,重点从结构体cef_zip_reader_t中的openfile成员函数的参数进行获取。
函数声明和相关结构体声明///// All ref-counted framework structures must include this structure first.///typedef struct _cef_base_ref_counted_t { /// // Size of the data structure. /// size_t size; /// // Called to increment the reference count for the object. Should be called // for every new copy of a pointer to a given object. /// void(CEF_CALLBACK* add_ref)(struct _cef_base_ref_counted_t* self); /// // Called to decrement the reference count for the object. If the reference // count falls to 0 the object should self-delete. Returns true (1) if the // resulting reference count is 0. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* release)(struct _cef_base_ref_counted_t* self); /// // Returns true (1) if the current reference count is 1. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* has_one_ref)(struct _cef_base_ref_counted_t* self); /// // Returns true (1) if the current reference count is at least 1. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* has_at_least_one_ref)(struct _cef_base_ref_counted_t* self);} cef_base_ref_counted_t; ///// Structure that supports the reading of zip archives via the zlib unzip API.// The functions of this structure should only be called on the thread that// creates the object.///typedef struct _cef_zip_reader_t { /// // Base structure. /// cef_base_ref_counted_t base; /// // Moves the cursor to the first file in the archive. Returns true (1) if the // cursor position was set successfully. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* move_to_first_file)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self); /// // Moves the cursor to the next file in the archive. Returns true (1) if the // cursor position was set successfully. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* move_to_next_file)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self); /// // Moves the cursor to the specified file in the archive. If |caseSensitive| // is true (1) then the search will be case sensitive. Returns true (1) if the // cursor position was set successfully. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* move_to_file)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self, const cef_string_t* fileName, int caseSensitive); /// // Closes the archive. This should be called directly to ensure that cleanup // occurs on the correct thread. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* close)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self); // The below functions act on the file at the current cursor position. /// // Returns the name of the file. /// // The resulting string must be freed by calling cef_string_userfree_free(). cef_string_userfree_t(CEF_CALLBACK* get_file_name)( struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self); /// // Returns the uncompressed size of the file. /// int64(CEF_CALLBACK* get_file_size)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self); /// // Returns the last modified timestamp for the file. /// cef_basetime_t(CEF_CALLBACK* get_file_last_modified)( struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self); /// // Opens the file for reading of uncompressed data. A read password may // optionally be specified. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* open_file)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self, const cef_string_t* password); /// // Closes the file. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* close_file)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self); /// // Read uncompressed file contents into the specified buffer. Returns < 0 if // an error occurred, 0 if at the end of file, or the number of bytes read. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* read_file)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self, void* buffer, size_t bufferSize); /// // Returns the current offset in the uncompressed file contents. /// int64(CEF_CALLBACK* tell)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self); /// // Returns true (1) if at end of the file contents. /// int(CEF_CALLBACK* eof)(struct _cef_zip_reader_t* self);} cef_zip_reader_t; ///// Writes the contents of |src_dir| into a zip archive at |dest_file|. If// |include_hidden_files| is true (1) files starting with "." will be included.// Returns true (1) on success. Calling this function on the browser process UI// or IO threads is not allowed.///CEF_EXPORT int cef_zip_directory(const cef_string_t* src_dir, const cef_string_t* dest_file, int include_hidden_files); ///// Create a new cef_zip_reader_t object. The returned object's functions can// only be called from the thread that created the object.///CEF_EXPORT cef_zip_reader_t* cef_zip_reader_create( struct _cef_stream_reader_t* stream);
那么我就有思路了,首先断点只会断一次,所以我们不需要考虑解密函数的参数变化问题,因为它只会解密这一个zip,因此我的思路如下:
1.在cef_zip_reader_create下断点。
2.命中断点后,执行到返回,返回值就是cef_zip_reader_t结构体的指针。
3.拿到指针地址,咱们就拿到了openfile函数的地址。
4.在openfile函数下断点,断点命中后,直接在栈上看第二个参数即可(如果不确定人家的调用约定的话,那就也看看寄存器,万一是fastcall呢)。
最终在第二个参数拿到了一串字符串,作为密码,成功解压!(密码就不展示了)里面包含了挺多功能:添加联系人、搜索、设置等等相关的html和js资源。
所以目前我对CEF框架应用的一个理解,大概是它们的界面、操作等等代码都是用html、js语言去实现的,相当于把一个在线网页做成了客户端(难怪以前用OD咋都断不到MessageBox,合着人家压根就没用C++实现,终于明白了)。
我们如果想对该应用的代码逻辑进行相关修改的话:
1.直接改zip里的js或者html文件,事不宜迟,先试试看效果。
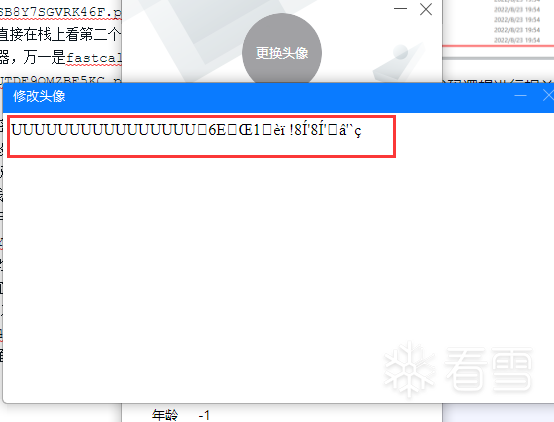
我这里把修改头像的一个html页面给改了点东西,替换进zip里。
然后重新启动如流,登录,进入头像修改页面,结果直接给我乱码了。然后尝试了下啥也不改,只要是替换了,就会乱码。凉凉,估计加载资源文件的时候有校验,比如它的修改时间、MD5、编码等等。不过还是证明了修改文件会造成影响。
2.从内存里进行修改。
五
开启CEF框架调试功能
在 cef_browser_host_t结构体中有一个show_dev_tools成员,可以用来开启调试窗口。
cef_browser_host_t对象可以通过cef_browser_t的get_host拿到,而cef_browser_t会在CEF的事件处理回调函数中作为参数传入,所以这里就要使用detours写hook代码了,去hook事件处理回调函数,代码如下:// dllmain.cpp : 定义 DLL 应用程序的入口点。#include "pch.h"#include "detours/detours.h"#include "include/capi/cef_browser_capi.h"#include "include/internal/cef_types_win.h"#include "include/capi/cef_client_capi.h"#include "include/internal/cef_win.h"#include <Windows.h> PVOID g_cef_browser_host_create_browser = nullptr VOID g_cef_get_keyboard_handler = NULL VOID g_cef_get_keyboard_handler = NULL VOID g_cef_on_key_event = NULL; void SetAsPopup(cef_window_info_t* window_info) { window_info->style = WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW | WS_CLIPCHILDREN | WS_CLIPSIBLINGS | WS_VISIBLE; window_info->parent_window = NULL; window_info->x = CW_USEDEFAULT; window_info->y = CW_USEDEFAULT; window_info->width = CW_USEDEFAULT; window_info->height = CW_USEDEFAULT;} int CEF_CALLBACK hook_cef_on_key_event( struct _cef_keyboard_handler_t* self, struct _cef_browser_t* browser, const struct _cef_key_event_t* event, cef_event_handle_t os_event) { OutputDebugStringA("[detours] hook_cef_on_key_event \n"); auto cef_browser_host = browser->get_host(browser); // 键盘按下且是F12 if (event->type == KEYEVENT_RAWKEYDOWN && event->windows_key_code == 123) { cef_window_info_t windowInfo{}; cef_browser_settings_t settings{}; cef_point_t point{}; SetAsPopup(&windowInfo); OutputDebugStringA("[detours] show_dev_tools \n"); // 开启调试窗口 cef_browser_host->show_dev_tools (cef_browser_host, &windowInfo, 0, &settings, &point); } return reinterpret_cast<decltype(&hook_cef_on_key_event)> (g_cef_on_key_event)(self, browser, event, os_event);} struct _cef_keyboard_handler_t* CEF_CALLBACK hook_cef_get_keyboard_handler( struct _cef_client_t* self) { OutputDebugStringA("[detours] hook_cef_get_keyboard_handler \n"); // 调用原始的修改get_keyboard_handler函数 auto keyboard_handler = reinterpret_cast<decltype(&hook_cef_get_keyboard_handler)> (g_cef_get_keyboard_handler)(self); if (keyboard_handler) { // 记录原始的按键事件回调函数 g_cef_on_key_event = keyboard_handler->on_key_event; // 修改返回值中的按键事件回调函数 keyboard_handler->on_key_event = hook_cef_on_key_event; } return keyboard_handler;} int hook_cef_browser_host_create_browser( const cef_window_info_t* windowInfo, struct _cef_client_t* client, const cef_string_t* url, const struct _cef_browser_settings_t* settings, struct _cef_dictionary_value_t* extra_info, struct _cef_request_context_t* request_context) { OutputDebugStringA("[detours] hook_cef_browser_host_create_browser \n"); // 记录原始的get_keyboard_handler g_cef_get_keyboard_handler = client->get_keyboard_handler; // 修改get_keyboard_handler client->get_keyboard_handler = hook_cef_get_keyboard_handler; return reinterpret_cast<decltype(&hook_cef_browser_host_create_browser)> (g_cef_browser_host_create_browser)( windowInfo, client, url, settings, extra_info, request_context);} // Hook cef_browser_host_create_browserBOOL APIENTRY InstallHook(){ OutputDebugStringA("[detours] InstallHook \n"); DetourTransactionBegin(); DetourUpdateThread(GetCurrentThread()); g_cef_browser_host_create_browser = DetourFindFunction("libcef.dll", "cef_browser_host_create_browser"); DetourAttach(&g_cef_browser_host_create_browser, hook_cef_browser_host_create_browser); LONG ret = DetourTransactionCommit(); return ret == NO_ERROR;} BOOL APIENTRY DllMain( HMODULE hModule, DWORD ul_reason_for_call, LPVOID lpReserved ){ switch (ul_reason_for_call) { case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH: InstallHook(); break; case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH: case DLL_THREAD_DETACH: case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH: break; } return TRUE;} VOID g_cef_on_key_event = NULL; void SetAsPopup(cef_window_info_t* window_info) { window_info->style = WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW | WS_CLIPCHILDREN | WS_CLIPSIBLINGS | WS_VISIBLE; window_info->parent_window = NULL; window_info->x = CW_USEDEFAULT; window_info->y = CW_USEDEFAULT; window_info->width = CW_USEDEFAULT; window_info->height = CW_USEDEFAULT;} int CEF_CALLBACK hook_cef_on_key_event( struct _cef_keyboard_handler_t* self, struct _cef_browser_t* browser, const struct _cef_key_event_t* event, cef_event_handle_t os_event) { OutputDebugStringA("[detours] hook_cef_on_key_event \n"); auto cef_browser_host = browser->get_host(browser); // 键盘按下且是F12 if (event->type == KEYEVENT_RAWKEYDOWN && event->windows_key_code == 123) { cef_window_info_t windowInfo{}; cef_browser_settings_t settings{}; cef_point_t point{}; SetAsPopup(&windowInfo); OutputDebugStringA("[detours] show_dev_tools \n"); // 开启调试窗口 cef_browser_host->show_dev_tools (cef_browser_host, &windowInfo, 0, &settings, &point); } return reinterpret_cast<decltype(&hook_cef_on_key_event)> (g_cef_on_key_event)(self, browser, event, os_event);} struct _cef_keyboard_handler_t* CEF_CALLBACK hook_cef_get_keyboard_handler( struct _cef_client_t* self) { OutputDebugStringA("[detours] hook_cef_get_keyboard_handler \n"); // 调用原始的修改get_keyboard_handler函数 auto keyboard_handler = reinterpret_cast<decltype(&hook_cef_get_keyboard_handler)> (g_cef_get_keyboard_handler)(self); if (keyboard_handler) { // 记录原始的按键事件回调函数 g_cef_on_key_event = keyboard_handler->on_key_event; // 修改返回值中的按键事件回调函数 keyboard_handler->on_key_event = hook_cef_on_key_event; } return keyboard_handler;} int hook_cef_browser_host_create_browser( const cef_window_info_t* windowInfo, struct _cef_client_t* client, const cef_string_t* url, const struct _cef_browser_settings_t* settings, struct _cef_dictionary_value_t* extra_info, struct _cef_request_context_t* request_context) { OutputDebugStringA("[detours] hook_cef_browser_host_create_browser \n"); // 记录原始的get_keyboard_handler g_cef_get_keyboard_handler = client->get_keyboard_handler; // 修改get_keyboard_handler client->get_keyboard_handler = hook_cef_get_keyboard_handler; return reinterpret_cast<decltype(&hook_cef_browser_host_create_browser)> (g_cef_browser_host_create_browser)( windowInfo, client, url, settings, extra_info, request_context);} // Hook cef_browser_host_create_browserBOOL APIENTRY InstallHook(){ OutputDebugStringA("[detours] InstallHook \n"); DetourTransactionBegin(); DetourUpdateThread(GetCurrentThread()); g_cef_browser_host_create_browser = DetourFindFunction("libcef.dll", "cef_browser_host_create_browser"); DetourAttach(&g_cef_browser_host_create_browser, hook_cef_browser_host_create_browser); LONG ret = DetourTransactionCommit(); return ret == NO_ERROR;} BOOL APIENTRY DllMain( HMODULE hModule, DWORD ul_reason_for_call, LPVOID lpReserved ){ switch (ul_reason_for_call) { case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH: InstallHook(); break; case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH: case DLL_THREAD_DETACH: case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH: break; } return TRUE;}
然后注入的话,我先是使用detours的注入功能:setdll /d:E:\VS_DEBUG\DetoursDll\Debug\DetoursDll.dll D:\infoflow\infoflow.exe
原理其实就是把dll给注入到exe的节表里了,运行失败,估计对exe有校验。
于是我在exe运行的时候,使用远程线程注入dll,成功。
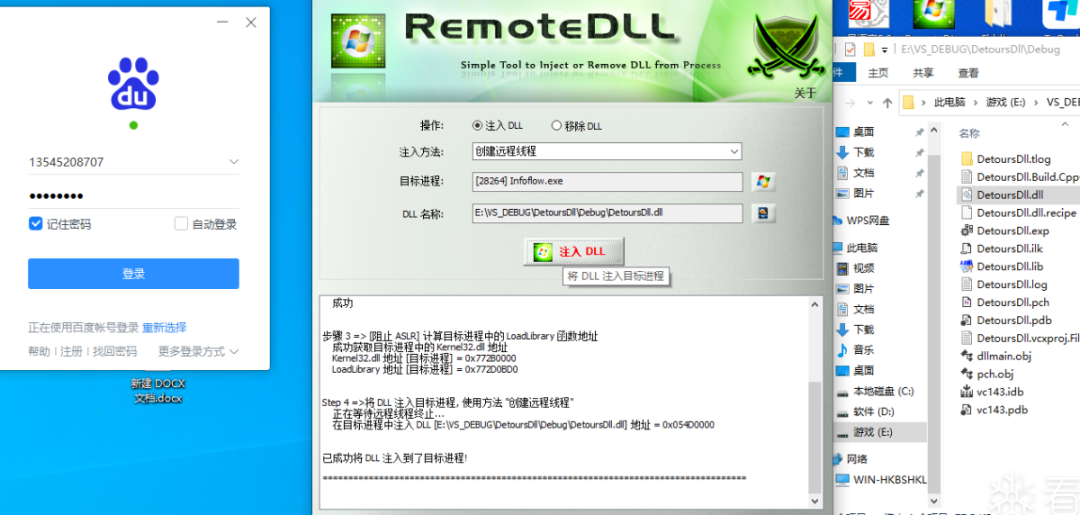
登录进去,尝试在某些页面里,按F12,可以开启Chrome调试窗口,非常的方便。
六
尝试做点什么功能+总结(未遂)
可惜的是,在聊天窗口里面,怎么按F12都不管用,资源文件里好像也确实没有聊天框相关的html,哎,本来想学着参考帖做一个防撤回工具的,结果聊天框压根就不是用前端语言写的,所以不能用CEF框架的调试功能去定位关键代码了。
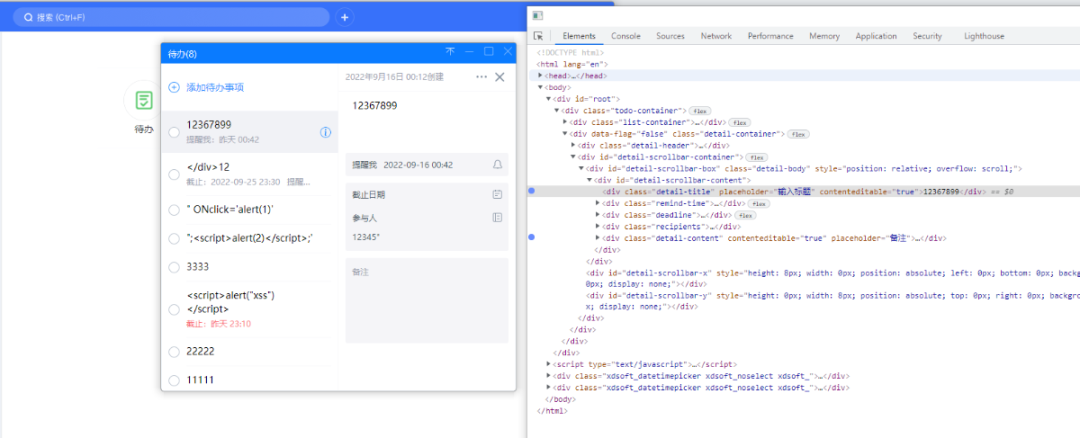
但毕竟整了这么久,多少得干点啥吧,干脆在这里借用CEF框架,给大家普及一下XSS漏洞吧。可以看到“待办”这个页面,可以进行一个输入、保存,通过Chrome调试页面可知,保存时,会将内容发送给服务器,那么如果我们去输入javascript脚本是否能触发xss反射型漏洞呢?

看了下页面元素构成,很明显不行,因为值是以文本形式夹在div标签里面,并不能触发脚本语言。

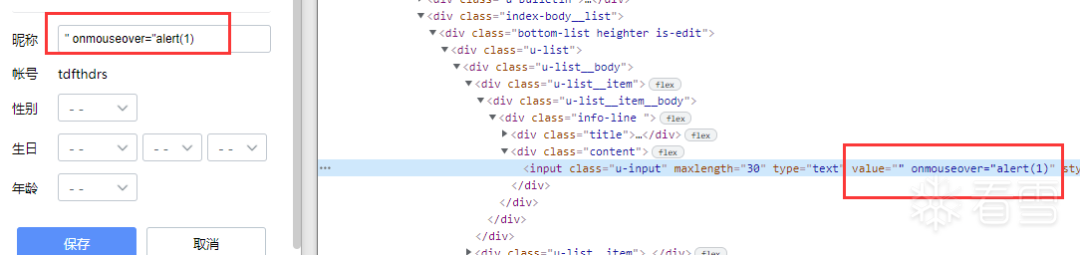
那好吧,我去找个存放在标签里面的值修改吧,可以看到,昵称是会写到value值下的。

那我们把它改成攻击代码,将value用"给闭合,然后设置一个鼠标事件,当鼠标移动到框内时,就会弹窗。
结果并没有弹,查看html源码,发现"已经被编码成"
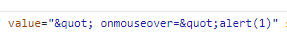
看来安全措施做的挺到位嘛,那我也就止步于此了。
总结下来,了解到了CEF框架的一些关键数据结构和api,达到解密资源文件的一个效果。然后也学会了detours的hook功能,使用静态或动态注入的手段。
|
|
 |Archiver|手机版|小黑屋|firemail
( 粤ICP备15085507号-1 )
|Archiver|手机版|小黑屋|firemail
( 粤ICP备15085507号-1 )